A video generator's lifecycle
The video generator lifecycle is the same as that of an event tagger. Feel free to skip this section if you're already familiar with it.
Each generator and its versions have a lifecycle that includes the following steps:
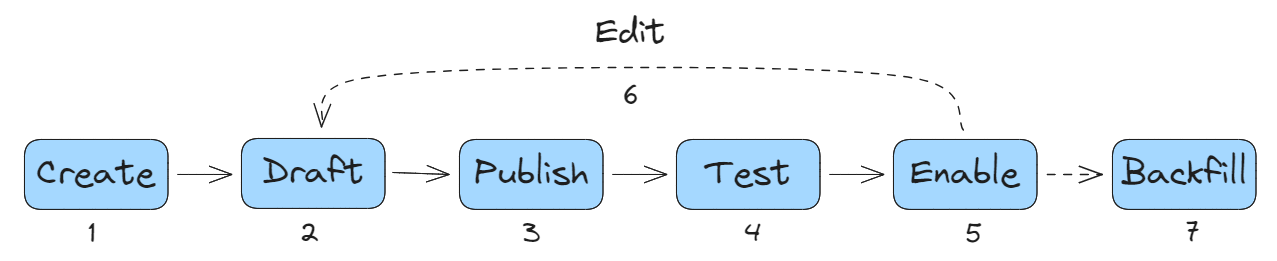
1. Create
The generator is created with a unique name and an optional description. Newly created generators are disabled by default and cannot be enabled until a generator version is created, published, and successfully tested.
2. Draft
A new generator version with corresponding generator definition may be drafted and saved before being published. The latest published version is used as a starting point for new drafts when creating a draft in the web UI.
3. Publish
The last step to preparing a generator version for invocation is to publish/finalize it. Once published, a generator version's YAML definition is immutable and may not be edited. A new draft version must be created if you wish to make changes to the YAML definition.
4. Test
Test invocations are used to verify that the generator works as expected before it may be applied to a large number of robologs.
Here are rules enforced by our platform that pertain to a generator version's test status:
- You must successfully test a generator version before it may be used for any other types of invocation.
- Requests for kicking off a backfill invocation of an untested generator version will fail.
- A generator cannot be enabled if a successfull tested generator version does not exist for that generator.
- Normfill invocations of an enabled generator kicked off for each newly ingested robolog use the latest, successfully tested generator version available—not necessarily the latest published version.
5. Enable
Enabling a generator allows normfill invocations to automatically run for each new robolog that is ingested.
6. Edit
As you work with a generator, you may find that you need to make changes to its definition. This process involves creating a new draft version, making the necessary changes, publishing, and testing the new version.
7. Backfill
A backfill allows you to run the generator against robologs that have previously been ingested. Backfill invocations must be manually triggered.